Problem:Bragg scattering from non-Bravais lattices
We will here continue to investigate the nuclear structure factor, but this time for non-Bravais lattices.
Question 1
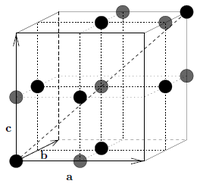
The NaCl crystal structure consists of two interpenetrating fcc sublattices (side length \(a\)) displaced by half a cube diagonal with respect to each other. The Na atoms are placed on the lattice sites of one of the lattices and the Cl atoms on the lattice site of the other. What are the relative coordinates of the Na and Cl atoms, respectively?
The NaCl lattice consists of two \(fcc\) lattices, one placed half a cube diagonal away. Hence
\begin{align} \mathbf{d}_{Na} &\in \left\{ (0,0,0), a\left(\dfrac{1}{2}, \dfrac{1}{2},0\right), a\left(\dfrac{1}{2},0, \dfrac{1}{2}\right),a\left(0,\dfrac{1}{2}, \dfrac{1}{2}\right)\right\} \\ \mathbf{d}_{Cl} &= \left(\mathbf{d}_{Na}+ a\left(\dfrac{1}{2}, \dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\right) \in \left\{ a\left(\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{1}{2}\right), a\left(0,0,\dfrac{1}{2}\right), a\left(0,\dfrac{1}{2},0\right),a\left(\dfrac{1}{2},0,0\right)\right\} \end{align}
which is illustrated in Figure xx--CrossReference--fig:NaCl--xx.
Question 2
The NaCl crystal may also be constructed by placing Na and Cl atoms alternating on a simple cubic lattice with side length \(a\). What is the side length (lattice parameter) of the combined structure? How many simple cubic lattices are needed for the NaCl structure? What are the relative coordinates of the Na and Cl atoms in this unit cell?
The sidelength of a combined sc structure with alternating Na and Cl atoms is \(2a\), so 8 simple cubes are needed. The relative coordinates in the combined unit cell are
\begin{equation} \mathbf{d}_{Cl} = \mathbf{d}_{Na}+ a(1,1,1) \end{equation}
Question 3
Calculate the expression for the structure factor of the NaCl crystal structure. Which reflections are allowed? What causes the difference between the structure factor of the allowed reflections?
The atomic basisvectors are written in 1. and the reciprocal lattice vector is \(\mathbf{\tau}=h\mathbf{a}^*+k\mathbf{b}^*+l\mathbf{c}^*\) with \(\mathbf{a}^*= \frac{2\pi}{a}(1,0,0)\), \(\mathbf{b}^*= \frac{2\pi}{a}(0,1,0)\) and \(\mathbf{c}^*= \frac{2\pi}{a}(0,0,1)\).
\begin{align} |F_N(hkl)|^2 &= \left|\displaystyle\sum_{\mathbf{d}_i^{Na}} e^{i \mathbf{\tau} \cdot \mathbf{d}_{Na} }\left( b_{Na}+ b_{Cl}e^{i {\boldsymbol\tau}\cdot a(\frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{2})}\right)\right|^2\\ & \left|\left( 1 + e^{i \pi (h+k)} + e^{i \pi (k+l)}+e^{i \pi (h+l)} \right)\times\left(b_{Na}+ b_{Cl}e^{i \pi (h+k+l)}\right)\right|^2\\ &= \begin{cases} 16|b_{Na}+b_{Cl}|^2 &\text{if all h,k,l even}\\ 16|b_{Na}-b_{Cl}|^2 &\text{if all h,k,l odd}\\ 0 & \text{else}\end{cases} \end{align}
since \(b_{Na}=3.63\cdot10^{-15}\text{m}^2\) and \(b_{Cl}=9.58\cdot10^{-15}\text{m}^2\) so the intensity from reflections where all \(h,k,l\) even is bigger than the intensity at \(h,k,l\) odd.
Question 4
The crystal structure of CeSb is also the NaCl structure. Why are the structure factors of some reflections almost zero?
CeSb is also the NaCl structure but since \(b_{Ce}=4.84\) fm and \(b_{Sb}=5.57\) fm then \(F_N(hkl)\approx 0\) for all \(h,k,l\) odd.
Question 5
Another compound of the sodium chloride structure is LiH. Calculate the squared structure factors of the three shortest allowed scattering vectors. What happens to the mean scattering length, \(\bar{b}\), for H if the naturally occuring H is enriched with 17 % D? Which consequences does that have for the structure factors, and how do you understand that?
LiH is also the NaCl structure, the 3 allowed reflections with the shortest $q$'s are (200), (111), (220) and the similar ones.
\begin{align} |F_N(200)|^2 &= |F_N(020)|^2 = |F_N(002)|^2 = 16|b_{Li}+b_H|^2 = 16(-1.90-3.742)^2\text{fm}^2 = 509 \rm{fm}^2\\ |F_N(111)|^2 &=|F_N(-1-1-1)|^2 = |F_N(-1-11)|^2 = |F_N(-111)|^2 = |F_N(-11-1)|^2 = |F_N(1-11)|^2\\ &= |F_N(11-1)|^2= |F_N(1-1-1)|^2 = 16(-1.90+3.742)^2 \rm{fm}= 54.3 \rm{fm}^2\\ |F_N(220)|^2 &= |F_N(-2-20)|^2 = |F_N(-220)|^2 =|F_N(2-20)|^2 = |F_N(022)|^2 = |F_N(0-2-2)|^2 \\ &= |F_N(0-22)|^2 = |F_N(02-2)|^2= |F_N(20 2)|^2 = |F_N(-2 0-2)|^2 \\ &= |F_N(20-2)|^2 = |F_N(-202)|^2 = 16(-1.90-3.742)^2 \rm{fm}^2=509 \rm{fm}^2 \end{align}
If the hydrogen consists of two isotopes (\(^{1}H\) and D=\(^{2}\)H) with abundance 0.17 % of D then the average scattering length is
\begin{equation} \overline{b}_H = a_Db_D+a_H+b_H = 0.17\cdot6.674 + (1-0.17)\cdot -3.742 = -1.972 \end{equation}
So if the LiH is doped with 17 % \(\overline{b}_H\approx b_{Li}\) and the structure factor for \(h,k,l\) odd vanishes.
Question 6
Si and Ge has the same structure as diamond where the atoms are placed in two interpenetrating fcc lattices (side length \(a\)). One of the lattices is displaced by \(1/4\) body diagonal with respect to the other, \({\bf d} = (1/4, 1/4, 1/4)a\). What is the distance between nearest neighbour sites?
Calculate the structure factor of the diamond cubic structure of Si. Which reflections are allowed? Do they have different structure factors? Can you think of some familiarities between the NaCl and the diamond structure?
The diamond structure is two \(fcc\) lattice where one is displaced by 1/4 body diagonal so
\begin{equation} \mathbf{d}_{i}^{\rm{Si}} \in \left\{ \mathbf{d}_{fcc},\mathbf{d}_{fcc}+a\left(\dfrac{1}{4},\dfrac{1}{4},\dfrac{1}{4}\right) \right\} \end{equation}
The nearest-neighbor distance is
\begin{equation} d = \sqrt{\left(\dfrac{a}{4}\right)^2 +\left(\dfrac{a}{4}\right)^2+ \left(\dfrac{a}{4}\right)^2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}a}{4} \end{equation}
so
\begin{align} |F_N(hkl)|^2 &= b_{Si}^2 \left|\left(1 + e^{i \pi (h+k)} + e^{i \pi (h+k)} + e^{i \pi (k+l)}+e^{i \pi (h+l)}\right)\times \left( 1 + e^{i \frac{\pi}{2}(h+k+l)}\right) \right|^2\\ &= \begin{cases} 64\ b_{Si}^2 &\text{if all h,k,l even and } h+k+l\neq 2(m+1)\\ 32\ b_{Si}^2 &\text{if all h,k,l odd }\\ 0 & \text{else}\end{cases} \end{align}
where \(m\) is an even number or zero. I.e. the (222) reflection is not allowed meaning that no second order scattering will be observed from setting the spectrometer to first order scatting off the (111) point.
Question 7
Why is it impossible to define a geometrical structure factor for NaCl and other compounds containing more than one element?
A geometrical structure factor for compounds containing more than one atom cannot be defined since the atoms cannot be at the same position and their relative positions will always moderate the scattering lengths.
Question 8
Neutron scattering lengths can be positive or negative. Describe the effect on the nuclear structure factor at a Bragg reflection, when the crystal contains an atom with a positive scattering length on one site and an atom with a negative scattering length on another site? What would the effect be on the nuclear structure factor, if the atoms hypothetically were placed on the same site?
If the crystal contains two atoms on different sites displaced by \(\mathbf{\Delta}\), the structure factor is
\begin{align} |F_N(\mathbf{q})|^2 &=(b_1+b_2e^{i\mathbf{q}\cdot \mathbf{\Delta}})(b_1+b_2e^{-i\mathbf{q}\cdot \mathbf{\Delta}})\\ &=b_1^2+b_2^2+2b_1b_2\cos(i\mathbf{q}\cdot \mathbf{\Delta})\\ \end{align}
In case the scattering lengths are the same \(b_2=b_1=b\)
\begin{equation} |F_N(\mathbf{q})|^2=2b^2(1+\cos(i\mathbf{q}\cdot \mathbf{\Delta})) \end{equation}
In case the scattering lengths are positive on one site and negative on the other such that \(b_2=-b_1=-b\)
\begin{equation} |F_N(\mathbf{q})|^2=2b^2(1-\cos(i\mathbf{q}\cdot \mathbf{\Delta})) \end{equation}
hence having a negative scattering length on one site corresponds to a phase shift of \(\pi\).
If the atoms were on the same site with opposite scattering lengths the structure factor would be zero.