Problem:The moderator temperature: Difference between revisions
ucph>Tommy (Created page with "In typical sources for neutron scattering purposes, the neutrons are moderated by water. These "thermal" neutrons will (almost) reach thermal equilibrium with the moderator. C...") |
m (Wikiadmin moved page Problem: The moderator temperature to Problem:The moderator temperature) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{hidden begin|toggle=right|title=Solution|titlestyle=background:#ccccff}} | {{hidden begin|toggle=right|title=Solution|titlestyle=background:#ccccff}} | ||
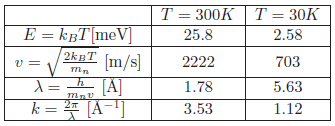
<figtable id="tab:specs_moderated_neutrons">[[File: | <figtable id="tab:specs_moderated_neutrons">[[File:Specs_moderated_neutrons.png|frame|<caption> Specifics for neutrons moderated at 30 K and 300 K.</caption>]]</figtable> | ||
The values shown are shown in <xr id="tab:specs_moderated_neutrons">Table %i</xr>. | The values shown are shown in <xr id="tab:specs_moderated_neutrons">Table %i</xr>. | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
\exp\big( {-C(T)(\lambda_1^{-2} -\lambda_2^{-2} )} \big) | \exp\big( {-C(T)(\lambda_1^{-2} -\lambda_2^{-2} )} \big) | ||
\end{equation*} | \end{equation*} | ||
where \( C(T) = h^2 / (2 m_n k_B T) \), hence | where \( C(T) = h^2 / (2 m_n k_B T) \), hence \(C(30\text{K}) = 3.17\times 10^{-19} \text{m}^2\) and \(C(300\text{K}) = 3.17\times 10^{-20}\text{m}^2\). | ||
So for \(T=30 \text{K}\) | So for \(T=30 \text{K}\) | ||
\begin{equation*} | \begin{equation*} | ||
\frac{I(4\tt{ | \frac{I(4\tt{Å})}{I(20\tt{Å})} | ||
= 5^5 \cdot \exp\big( -3.17\times 10^{-19}\cdot 6\times 10^{18} \big) | = 5^5 \cdot \exp\big( -3.17\times 10^{-19}\cdot 6\times 10^{18} \big) | ||
= 466 | = 466 | ||
\end{equation*} | \end{equation*} | ||
since | since \((4 \times 10^{-10} \text{m})^{-2} - (20 \times 10^{-10} \text{m})^{-2} = 6 \times 10^{18} \text{m}^{-2}\). | ||
For \(T=300 \text{K}\) | For \(T=300 \text{K}\) | ||
\begin{equation*} | \begin{equation*} | ||
\frac{I(4\tt{ | \frac{I(4\tt{Å})}{I(20\tt{Å})} | ||
= 5^5 \cdot \exp\big( {-3.17\times 10^{-20}\cdot 6\times 10^{18}} \big) | = 5^5 \cdot \exp\big( {-3.17\times 10^{-20}\cdot 6\times 10^{18}} \big) | ||
= 2584 | = 2584 | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
According to the calculation above apparantly there is several orders of magnitude more intensity of the neutrons at 4 Å than at 20 Å. If we however take a look at a small window of energies around 4 Å and 20 Å, respectively and integrate over these the ratios are not so extreme: | According to the calculation above apparantly there is several orders of magnitude more intensity of the neutrons at 4 Å than at 20 Å. If we however take a look at a small window of energies around 4 Å and 20 Å, respectively and integrate over these the ratios are not so extreme: | ||
Consider the intensity constant within the small wavelength bands | Consider the intensity constant within the small wavelength bands \(\lambda_1-\Delta \lambda_1; \lambda_1+\Delta \lambda_1\) and \(\lambda_2-\Delta \lambda_2; \lambda_2+\Delta \lambda_2\). The relative intensity between wavelength bands is | ||
\begin{equation*} | \begin{equation*} | ||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
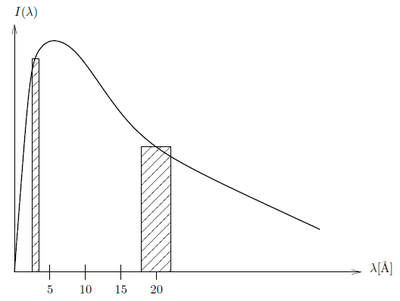
The approximation is shown in <xr id="fig:moderator_spectrum">Figure %i</xr>. | The approximation is shown in <xr id="fig:moderator_spectrum">Figure %i</xr>. | ||
If | If \({\Delta \lambda}/{\lambda}=10\%\) and \(\lambda_1=4\) Å and \(\lambda_2=20\) Å then \(\Delta\lambda_1=0.4\) Å and \(\Delta\lambda_2=2\) Å so at 30 K where \(I_1 / I_2 = I(4Å) / I(20Å) = 466\) | ||
\begin{equation*} | \begin{equation*} | ||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
\end{equation*} | \end{equation*} | ||
and at 300 K where | and at 300 K where \({I_1} / {I_2}={I(4Å)} / {I(20Å)} = 2584\) | ||
\begin{equation*} | \begin{equation*} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:25, 20 September 2020
In typical sources for neutron scattering purposes, the neutrons are moderated by water. These "thermal" neutrons will (almost) reach thermal equilibrium with the moderator. Calculate the equivalent energy, \(E\), and velocity, \(v\), of a thermal neutron, moderated by water at \(T_{{\rm H}_2 {\rm O}} = 300\,\text{K}\).
Question 1
Calculate the corresponding de Broglie wavelength, \(\lambda\), and wavenumber, \(k\).
The energy at a specific temperature is \( E = k_B T \) [meV] and the neutron velocity at a specific temperature is
\begin{equation*} v = \sqrt{\frac{2k_BT}{m_n}} \end{equation*}
with unit [m/s].
Use the constants \( m_n = 1.675 \times 10^{-27} \text{kg}\), \(1 \text{eV} = 1.602 \times 10^{-19} \text{J}\), \( k_B = 1.38 \times 10^{-23} \text{J/K} = 8.61 \times 10^{-5} \text{eV/K}\).
The de Broglie wavelength can be calculated from \(\lambda = h / (m_n v) \) [Å].
The calculated values can be found in the table of the solution of the next question.
Question 2
Perform the same calculations for neutrons thermalised by liquid H\(_2\) at \(T_H = 30 \text{K}\).
Question 3
For each of the two types of moderators above, calculate the ratio of intensities: \(I\)(4 Å)/\(I\)(20 Å).
\begin{equation*} \frac{I(\lambda_1)}{I(\lambda_2)} = \left(\frac{\lambda_2}{\lambda_1}\right)^5 \exp\big( {-C(T)(\lambda_1^{-2} -\lambda_2^{-2} )} \big) \end{equation*} where \( C(T) = h^2 / (2 m_n k_B T) \), hence \(C(30\text{K}) = 3.17\times 10^{-19} \text{m}^2\) and \(C(300\text{K}) = 3.17\times 10^{-20}\text{m}^2\).
So for \(T=30 \text{K}\)
\begin{equation*} \frac{I(4\tt{Å})}{I(20\tt{Å})} = 5^5 \cdot \exp\big( -3.17\times 10^{-19}\cdot 6\times 10^{18} \big) = 466 \end{equation*}
since \((4 \times 10^{-10} \text{m})^{-2} - (20 \times 10^{-10} \text{m})^{-2} = 6 \times 10^{18} \text{m}^{-2}\).
For \(T=300 \text{K}\)
\begin{equation*} \frac{I(4\tt{Å})}{I(20\tt{Å})} = 5^5 \cdot \exp\big( {-3.17\times 10^{-20}\cdot 6\times 10^{18}} \big) = 2584 \end{equation*}
Question 4
Many neutron instruments utilize a band of incident wavelength, \(\Delta \lambda\). For many instruments, \(\Delta \lambda / \lambda\) is almost constant and is of the order 0.1%-10%, depending on instrument type. For instruments with these bandwidths, calculate the ratio of the neutron fluxes at the sample: \(\Psi\)(4 Å)/\(\Psi\)(20 Å).
According to the calculation above apparantly there is several orders of magnitude more intensity of the neutrons at 4 Å than at 20 Å. If we however take a look at a small window of energies around 4 Å and 20 Å, respectively and integrate over these the ratios are not so extreme: Consider the intensity constant within the small wavelength bands \(\lambda_1-\Delta \lambda_1; \lambda_1+\Delta \lambda_1\) and \(\lambda_2-\Delta \lambda_2; \lambda_2+\Delta \lambda_2\). The relative intensity between wavelength bands is
\begin{equation*} \frac{I(\lambda_1\pm\Delta\lambda_1)}{I(\lambda_2\pm\Delta\lambda_2)} = \frac{\displaystyle\int_{\lambda_1-\Delta \lambda_1}^{\lambda_1+\Delta \lambda_1} I(\lambda_1)d\lambda_1} {\displaystyle\int_{\lambda_2-\Delta \lambda_2}^{\lambda_2+\Delta \lambda_2} I(\lambda_2)d\lambda_2} \approx \frac{I_1\cdot 2\Delta \lambda_1}{I_2\cdot 2\Delta \lambda_2} \end{equation*}
The approximation is shown in Figure xx--CrossReference--fig:moderator_spectrum--xx. If \({\Delta \lambda}/{\lambda}=10\%\) and \(\lambda_1=4\) Å and \(\lambda_2=20\) Å then \(\Delta\lambda_1=0.4\) Å and \(\Delta\lambda_2=2\) Å so at 30 K where \(I_1 / I_2 = I(4Å) / I(20Å) = 466\)
\begin{equation*} \frac{I(4\pm0.4)}{I(20\pm2)} = 466\frac{0.8}{4} = 93.2 \end{equation*}
and at 300 K where \({I_1} / {I_2}={I(4Å)} / {I(20Å)} = 2584\)
\begin{equation*} \frac{I(4\pm0.4)}{I(20\pm2)} = 2584\frac{0.8}{4} = 517 \end{equation*}